Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
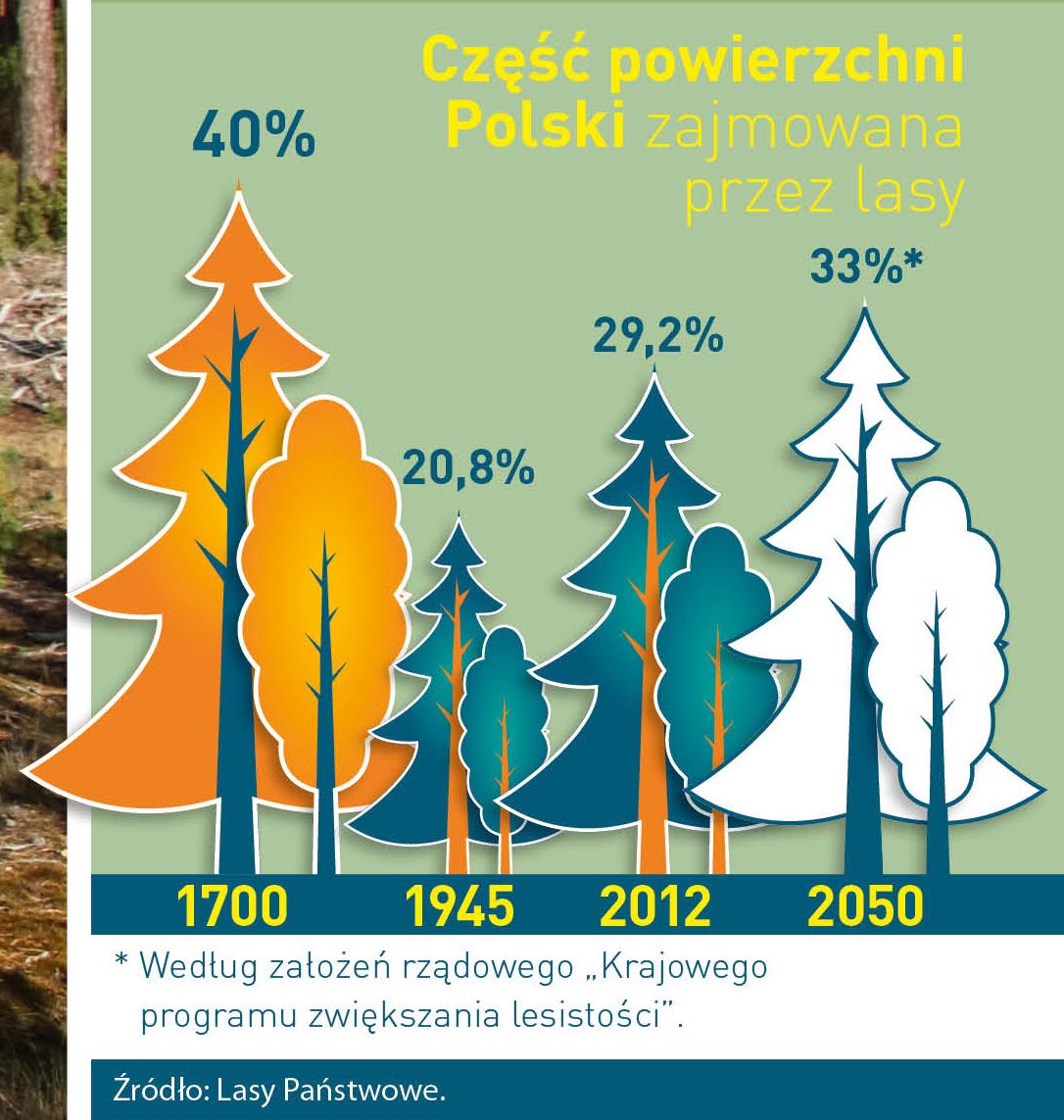
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
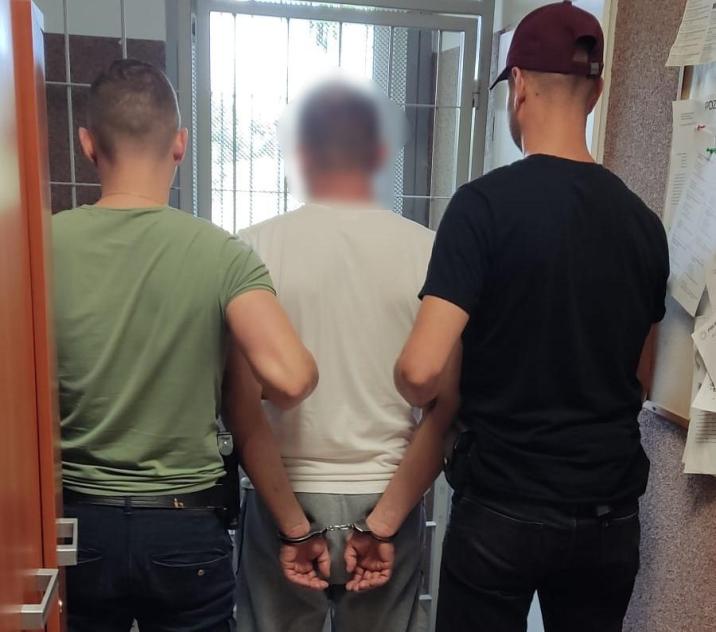
Kłusownicy w rękach Policji!
Kłusownicy w rękach Policji!
Policjanci z Komisariatu Policji w Pobiedziskach we współpracy ze Strażnikami Leśnymi z Nadleśnictwa Czerniejewo zatrzymali dwie osoby podejrzane o kłusownictwo.
Sprawa rozpoczęła się w kwietniu br., kiedy to policjanci otrzymali pierwszy sygnał od mieszkańców gminy Pobiedziska, o tym, że na terenach leśnych Parku Krajobrazowego w Promnie znaleziono skórę zabitego dzika, a kilkanaście metrów dalej jego pozostałości.
W związku z tym policjanci nawiązali współpracę z Posterunkiem Straży Leśnej Nadleśnictwa Czerniejewo, aby ustalić okoliczności tego zdarzenia. Dodatkowo, Strażnicy Leśni odkryli nielegalne nęcisko, które prawdopodobnie miało służyć zwabieniu dzikiej zwierzyny.
Po trzech miesiącach wspólnej, operacyjnej pracy nastąpił przełom w sprawie. Materiał dowodowy, jaki zebrali policjanci, był podstawą do wydania prokuratorskiego postanowienia o zatrzymaniu i przymusowym doprowadzeniu dwóch osób podejrzanych o kłusownictwo.
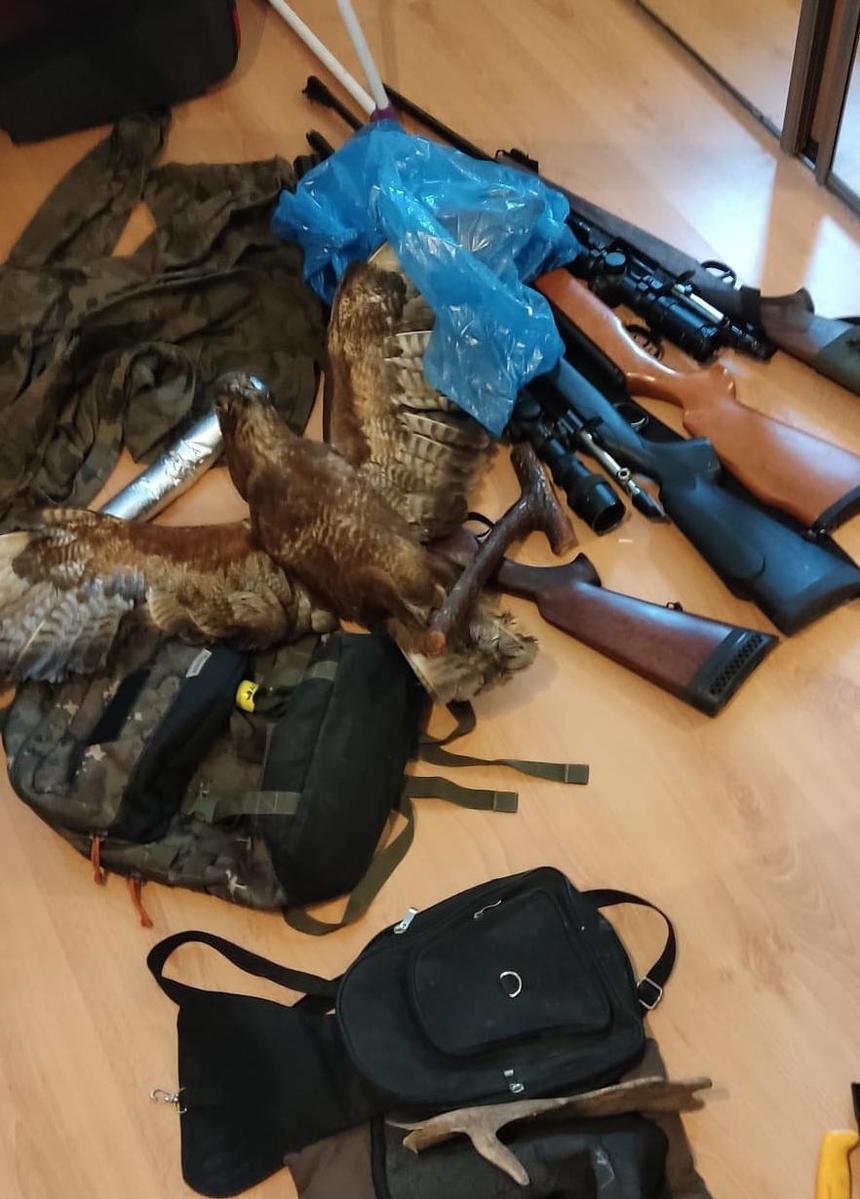

"W trakcie przeszukania policjanci zabezpieczyli 3 jednostki broni myśliwskiej, na które mężczyzna posiadał zezwolenie oraz wiatrówkę. Dodatkowo policjanci znaleźli specjalistyczny sprzęt termowizyjny i noktowizyjny, który służył sprawcom do obserwowania zwierzyny i jej odstrzału. Zabezpieczone zostały również narzędzia, które mogły im służyć do patroszenia upolowanej zwierzyny oraz truchła zwierząt – dzików, saren i jeleni." - informuje Marta Mróz z Komendy Miejskiej Policji w Poznaniu.
Obydwaj sprawcy, mieszkańcy gminy Pobiedziska, usłyszeli już prokuratorskie zarzuty prowadzenia polowania bez wymaganego zezwolenia oraz odstrzału dzika i przywłaszczenia zwierzęcia.
"Prawdopodobnie sprawa ta może mieć związek z ostatnimi przypadkami porzucenia w okolicznych lasach martwych szczątków zwierzyny. Na tym etapie śledztwa trudno jednak o jednoznaczne potwierdzenie tych podejrzeń. Z uwagi na dobro śledztwa pragniemy ograniczyć ewentualne przypuszczenia w przedmiotowej sprawie. Chcielibyśmy także zaznaczyć, że osiągnięte w toku prowadzonego śledztwa rezultaty nie byłyby możliwe bez wzorowej współpracy Strażników Leśnych Nadleśnictwa Czerniejewo z Komisariatem Policji w Pobiedziskach" - dodaje Hubert Kaczmarek, rzecznik prasowy Nadleśnictwa Czerniejewo.
"Do przypadków kłusownictwa na terenie RDLP w Poznaniu dochodzi rzadko, najczęściej Strażnicy Leśni walczą z nielegalnymi wjazdami do lasu i śmieceniem" - informuje Tomasz Maćkowiak, rzecznik prasowy RDLP w Poznaniu.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański